Electronic Medical Records (EMR) systems are used for efficient and effective patient care management. However, with the increasing reliance on these digital systems comes a significant challenge: ensuring the security and integrity of sensitive medical data. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, the intersection of EMR systems and cybersecurity has emerged as a critical area of focus. This report investigates the current technological landscape of EMR data security, exploring the latest advancements, prevalent challenges, and the evolving nature of cyber threats in the healthcare sector. Our objective is to provide a thorough analysis of current trends and technologies shaping the EMR cybersecurity space. By doing so, we aim to identify existing gaps and potential opportunities where further innovation is needed, and where strategic patent portfolio development and acquisition can play a pivotal role in advancing the security of EMR systems.
This landscape analysis serves not only as a barometer for the current state of EMR cybersecurity but also as a roadmap for future exploration and growth, opportunities for patenting, benefits from patent monetization and licensing in this vital field. We recognize that as EMR systems become increasingly integrated into healthcare infrastructures globally, the demand for robust cybersecurity solutions is at an all-time high. The report seeks to uncover potential ‘whitespaces’ - areas where innovation is scarce, but demand is high - offering unique opportunities for intellectual property development and acquisition. By pinpointing these opportunities, we aim to guide stakeholders, including healthcare providers, technology developers, and policymakers, towards areas where their efforts and investments can yield maximum impact in enhancing the resilience and security of EMR systems against the backdrop of an ever-evolving digital threat landscape.
This study covers an extensive review of the patent landscape to identify and analyze the breadth and depth of innovations in EMR security. A corpus of about 2,610 unique patent families (4207 total patents) was initially examined, from which 1,916 unique patent families were identified as pertinent to EMR security, through a rigorous process of triaging and relevancy analysis. These patents, spanning various jurisdictions globally, encompass a decade of innovation up to the year 2023, offering a comprehensive view of the technological evolution and whitespaces, opportunities in this critical field for companies who want to build or buy patents in this area of high growth.
The scope of the patents reviewed varied significantly, reflecting a broad spectrum of approaches to EMR security, from foundational encryption techniques to advanced, context-aware systems capable of real-time surveillance and threat mitigation. A detailed analysis of the claims and legal statuses of these patents provided insights into the technological trajectories and the maturation of security solutions over time. This analysis highlighted the dynamic nature of the field, with a steady influx of novel solutions aimed at addressing the complexities and vulnerabilities associated with EMR systems.
A notable aspect of the study was the geographical distribution of the patents, indicating a widespread recognition of the importance of EMR security across different regions. This geographical spread underscores the global challenge posed by EMR security and the diverse strategies employed to tackle it. Furthermore, the legal status of these patents revealed a highly competitive landscape, with a considerable number of active and enforceable patents indicating a robust environment of innovation and protection of intellectual property in the space of EMR security.
The study sheds light on the critical trends in EMR security technologies, delineating the evolution from basic security measures to sophisticated systems designed to preempt and counteract security breaches. This evolution reflects the escalating challenges in healthcare data security and the corresponding advancements in technology aimed at safeguarding patient information.
The data presented in the image below reflects the number of unique patent families filed per year related to electronic medical records (EMR) security technology. The information spans from 1999 to 2023, showing a clear trend in patent filing activity over the years.
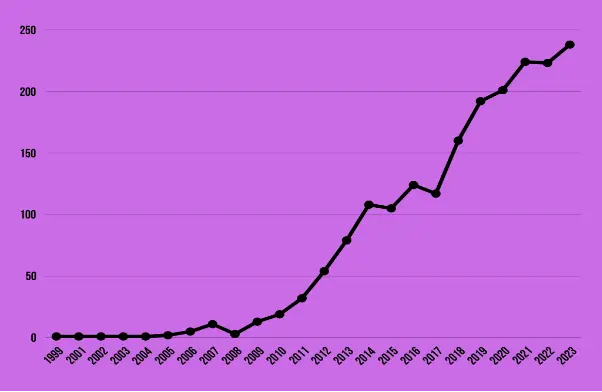
Initially, from 1999 to 2005, the patent activity in EMR security was minimal, with one or two filings per year, indicating either a nascent stage of technology or limited interest in securing electronic medical records. However, there is a notable increase starting in 2006, although the numbers remain low through 2008.
The period from 2009 to 2013 shows a gradual increase in patent filings, climbing from 13 to 79, which suggests a growing recognition of the importance of EMR security. The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) of 2009 played a pivotal role in driving the increase in EMR security patents filing during that period. The ARRA, through provisions such as the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, emphasized the importance of safeguarding patient information and mandated stricter security measures for EHR systems.
From 2014 onwards, there is a more pronounced upward trajectory. The year 2014 marked the crossing into significant counts with 108 filings, and by 2018, filings had increased to 160. This rise corresponds with the global push for digital health services and possibly reflects the escalating threats to data security, prompting more innovation in protective measures.
The most significant growth occurred from 2019 to 2023, with the number of filings jumping from 192 to a peak of 238. This period, notably including the years affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, may have accelerated the digital transformation in healthcare, necessitating advancements in EMR security technology. The data reveals an increased emphasis on innovation in this field, likely driven by the growing complexity of cyber threats and the expansion of telemedicine.
The peak in 2023 with 238 filings suggests that EMR security technology is a critical and rapidly evolving area within healthcare technology. The increase in patents may reflect ongoing efforts to address new challenges in data protection and to keep pace with the evolving landscape of digital health.
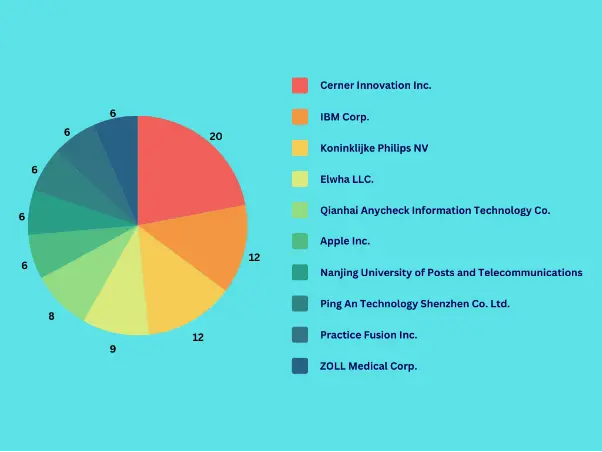
The landscape of patent filings in the electronic health record (EHR) technology space over the past decade reveals a competitive and innovative environment dominated by a mix of established tech giants, healthcare specialists, and emerging players. The about 2000 unique patent families data analysed by Intellectual Frontiers reveals interesting insights on the leaders in EHR tech innovation.
Cerner Innovation Inc., a company with a strong foothold in the healthcare technology sector, leads the pack with more than 20 unique patent families. This underscores Cerner’s commitment to advancing EHR technology, reflecting their strategic focus on enhancing healthcare IT solutions. Their leadership position in patent filings indicates a significant investment in research and development (R&D) to innovate and perhaps set industry standards in EHR security and functionality.
Following Cerner, IBM Corp, Koninklijke Philips, Allscripts, Epic all have filed significant number of patents. IBM’s presence highlights its broad technology expertise being applied within the healthcare sector, while Philips’ filings align with its focus on health technology solutions. These numbers show not only a dedication to securing patient data but also potentially point to advancements in integrating EHR systems with broader digital healthcare ecosystems.
The list includes a blend of other notable U.S.-based companies like Elwha LLC, Apple Inc., and Practice Fusion Inc., each bringing their unique expertise to the fore. Apple’s entry with top number of filings suggests an interest in integrating EHR technology with consumer devices, which is consistent with its expansion into health and wellness applications. Practice Fusion’s presence indicates a focus on cloud-based solutions, an area of significant growth in healthcare IT.

The data also highlights international and interdisciplinary collaboration with entries like Qianhai Anycheck Information Technology Co, indicating a global recognition of the importance of EHR technology. These entries, along with others like Ping An Technology and Nanjing University of Posts & Telecom, suggest that innovation in EHR is not confined to traditional healthcare markets or players, but is a field of interest across different sectors and regions.
The presence of diverse entities such as Siemens AG and F. Hoffmann-La Roche indicates a cross-industry push towards improving EHR tech, with these conglomerates possibly leveraging their broad expertise in engineering and pharmaceuticals, respectively, to contribute to the technological advancements in EHR systems. The variety of contributors from different backgrounds demonstrates that the future of EHR technology is likely to be shaped by multidisciplinary approaches to innovation, security, and patient-centric care.
The trends in patent filings across top industrial sectors suggest a clear emphasis on computer and digital technologies, reflecting the ongoing digital transformation across industries.
Leading the way is Computer Technology with a significant 993 filings, nearly double the number in the next category. This dominance indicates that the core of innovation lies in improving and creating new computing technologies, which are the backbone of modern devices, services, and systems. The high number of patent filings in this sector suggests a continuous push for development in software, hardware, and computational methods.
Digital Communication follows with 463 filings, underscoring the importance of advancements in the way we exchange information. This sector is crucial for the development of new protocols, systems, and technologies that enable efficient and secure communication across various platforms. The robust activity in this sector may be driven by the increasing demand for better and faster communication technologies in both personal and professional settings.
IT Methods for Management is also prominent with 331 filings, reflecting the need for sophisticated information technology solutions in business and organizational contexts. This suggests that companies are actively seeking new ways to improve efficiency, productivity, and management of resources through IT innovations.
The sectors of Control, Audio-Visual Technology, and Telecommunications, though having fewer filings, indicate niche areas of focused innovation. Control technologies are essential for automation and systems management, while Audio-Visual Technology and Telecommunications are vital for multimedia content delivery and communication infrastructure, respectively.
Overall, these trends highlight the key areas where technological advancements are being pursued aggressively, with computer technology and digital communication leading the charge. The range of filings across different sectors also reflects the breadth of innovation occurring as industries adapt to a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
In the current landscape of healthcare innovation, a discernible emphasis has been placed on the development of information and communication technology (ICT) that is specifically designed to process and manage individual patient data. This trend aligns with the increasing demand for personalized healthcare, where treatments and healthcare strategies are tailored to individual patient profiles, necessitating advanced data processing capabilities that can handle complex and sensitive patient data with precision and care.
Parallel to the surge in patient-centered ICT developments, there has been a substantial increase in patents filed for technologies that secure data access. These technologies are integral to the establishment of trust in digital healthcare platforms, as they ensure that sensitive patient information is protected against unauthorized access, thereby complying with stringent privacy regulations and maintaining the integrity of confidential health data.
The oversight and organization of healthcare resources also form a critical component of the recent patent filings. Innovations in this area suggest a move towards more streamlined healthcare operations, with technologies aiming to optimize the management of healthcare personnel, patient scheduling, surgical workflows, and the logistics of medical inventory. Such advances are indicative of a sector seeking to improve the efficacy and efficiency of healthcare delivery through sophisticated management systems.
There is a marked focus on the security of software systems within healthcare settings, with a considerable number of patents addressing the need for controlled access to executable software. These technologies are vital for the protection of healthcare systems from potential cyber threats, ensuring that both the software and the data it contains are safeguarded in a controlled environment.
The field of telemedicine has also seen an uptick in patent activity, with a variety of innovations aimed at remotely controlling medical devices and their interfaces. This reflects the growing trend towards remote healthcare delivery, where patients can receive care outside traditional clinical settings, thus requiring reliable and secure ICT systems that can manage medical devices from a distance.
Collectively, these trends demonstrate a robust and continuing commitment within the healthcare sector to leverage ICT for enhancing patient care, improving healthcare operations, and securing health data and systems. Such efforts are foundational to advancing healthcare delivery in an increasingly digital world, ensuring that patient care remains both effective and secure.
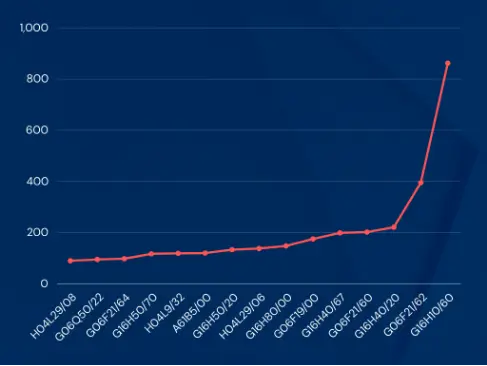
G16H10/60: Information and Communication Technology (ICT) tailored for processing data specific to individual patients.
G06F21/62: Methods for safeguarding data access through a specific platform.
G16H40/20: ICT designed for the oversight and organization of healthcare resources, such as managing staff, patients, surgical schedules, and medical inventories.
G06F21/60: Techniques for granting access to executable software, involving specific methods like code manipulation or ensuring program security, to protect data in a controlled setting.
G16H40/67: ICT developed for remotely controlling medical devices and their interfaces.
G06F19/00: Computing or data processing systems or methods optimized for particular functions or uses.
G16H80/00: ICT optimized to enhance communication among medical professionals or between doctors and patients, potentially for cooperative diagnosis, therapy, or health monitoring.
H04L29/06: Systems involving protocols for digital communication that are not specifically covered by other established categories.
G16H50/20: Systems for medical diagnosis or assistance in diagnosis, potentially utilizing expert medical systems for support.
A61B5/00: Methods and equipment for medical diagnosis and surgery, as well as tools for measuring bodily functions for diagnostic purposes.
H04L9/32: Cryptographic technologies focused on secure authentication and identification, including authorization and integrity checks.
G16H50/70: The process of extracting valuable information from medical data sets.
G06F21/64: Strategies and systems for maintaining the accuracy and consistency of data.
G06Q50/22: ICT aimed at providing services to engage individuals or communities to address societal or personal challenges or to enhance social welfare.
H04L29/08: Communication systems employing specific control procedures for data transmission that do not fall under established classifications.
