The Challenge with User Generated Electronic Data (UGED)
User Generated Electronic Data (UGED), termed as Consumer Generated Electronic Data (CGED), and also commonly referred to as user-generated data, forms a pivotal component in the vast electronic transactional aspect. Such data spans various forms such as historical records, biometric insights, electronic diagnosis outcomes, and data generated by devices connected to users. The expansive and diverse nature of UGED inherently poses challenges, particularly due to its heterogeneity and vast volume.
One primary concern arising from such diversity is the origin of the data itself. While some UGED might be sourced directly from the user, others may be provided on behalf of third parties, such as service providers or individuals associated with the user. This raises substantial questions regarding the authenticity, reliability, and completeness of the information. Given its pivotal role in decision-making processes, the ambiguity surrounding UGED’s accuracy becomes a critical concern. For instance, professionals, while making decisions based on UGED, might find themselves in a dilemma, either placing blind trust in the data or dismissing it entirely owing to its questionable reliability.
Amplification of Complexity with Biometric and Device Data
The integration of biometric or device-oriented data further exacerbates the challenge and with users gaining more control over various devices, like those for exercise, diet, or weight management, the UGED’s complexity grows manifold, concerns about the reliability, trustworthiness, clarity of authority, and responsibility for the data’s completeness and accuracy take center stage. The possibility of counterfeit data insertion, either by malicious entities or inadvertently, adds another layer of uncertainty. Such deceptive data can have profound repercussions, leading to flawed decision-making processes and, in extreme cases, compromising the entire transactional technology due to cyber threats like malware.
Existing Solutions and Their Limitations
Existing solutions primarily focus on user-generated data input into electronic transactional technologies. They ensure data reliability by setting predefined physiological value parameters. If data diverges from these norms, the user is prompted for verification. However, these solutions fall short when dealing with UGED that isn’t directly sourced from the user. Thus, a gap persists in assuring the reliability and completeness of externally sourced UGED.
Addressing the UGED Challenge
Metadata Analysis and Natural Language Processing for UGED Verification
To address the complexities and challenges surrounding UGED, the patented technology searches through metadata associated with the UGED. By storing this metadata in an electronic record repository database, the technology can apply advanced natural language processing and metadata analysis techniques. This sophisticated analysis segregates the data into two primary categories: user-verified data and user-unverified data.
Interactive Verification for Enhanced Accuracy
To bolster the authenticity of UGED, users engage with an interactive data object. This object features query statements and approval options. Users provide inputs in response to these queries, allowing them to authenticate and rectify any unverified data, ensuring its accuracy and authenticity.
Data Security and Trust Enhancement
After refining and verifying the user’s electronic data, it is incorporated into an advanced electronic transactional technology. This process enhances security and trust by ensuring data consistency and transparency.
In this process of electronic transactions, the significance of User Generated Electronic Data cannot be understated. By addressing its reliability and authenticity challenges, this innovative approach employs sophisticated techniques such as metadata analysis and natural language processing. The result is that UGED emerges as a pillar of trust and reliability within the electronic transactional domain.
Boosting Trust in User-Generated Electronic Data: An In-Depth Exploration of User-Generated Data Functionalities
Harnessing Wearable Devices
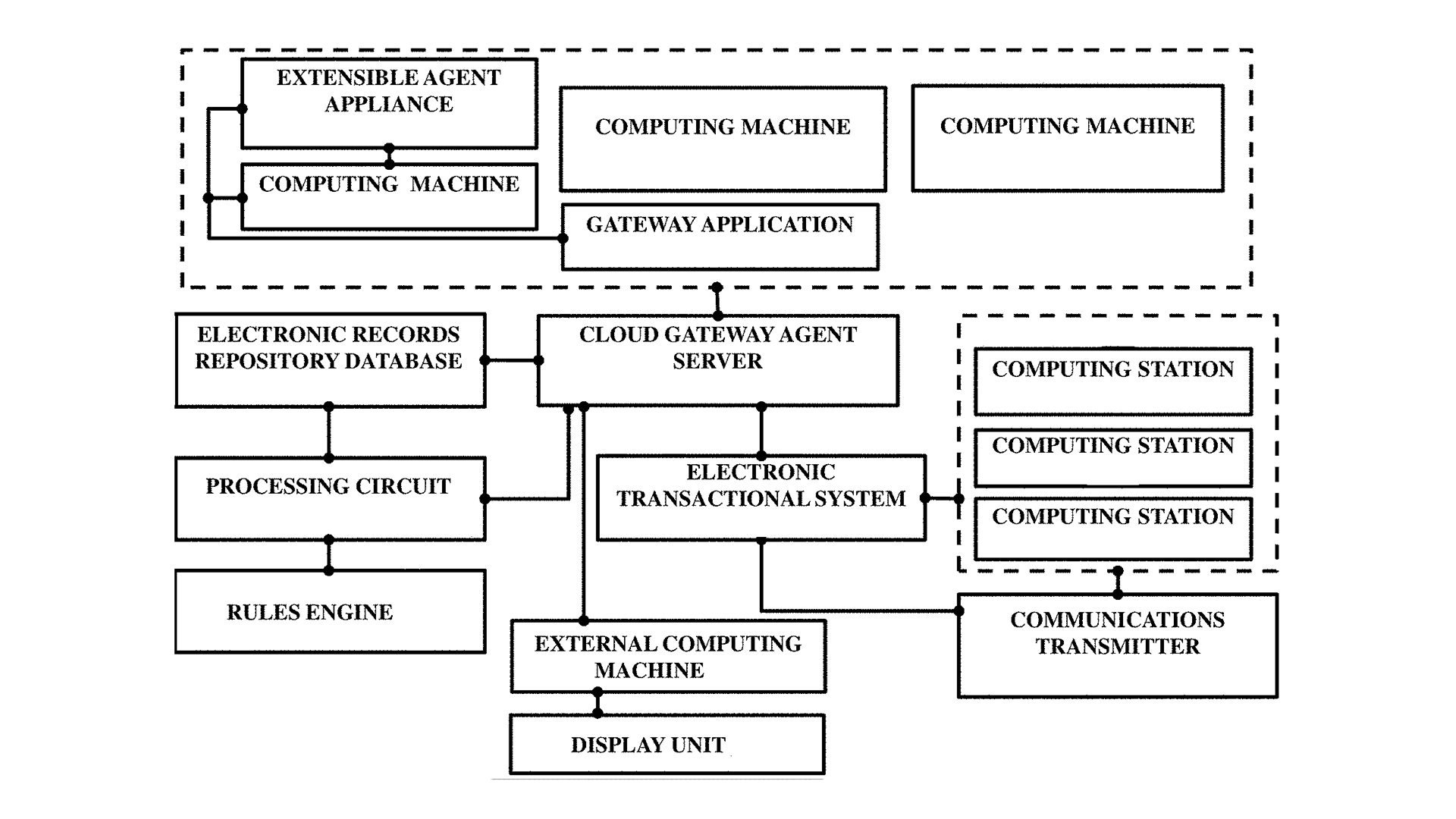
Modern users often sport a range of wearable devices and the developed technology efficiently leverages this ubiquity, aggregating user-generated electronic data from multiple such devices without requiring any user intervention. This data is not confined to simple inputs but expands to include intricate computer executable data files present in these wearables.
Cloud Connectivity and Data Storage
Once collected, this data funnels into a dedicated cloud gateway agent server, acting as a bridge between the wearable devices and a subsequent electronic record repository database. The latter securely holds both the collected data files and their associated metadata, preserving an intact account of user activities and data origins.
Intuitive Data Analysis
A cornerstone of the technology is its processing circuit through which it prowess in natural language processing and metadata analysis segregates the accumulated data into two distinct sets: those verified by users and those that remain unverified. This distinction plays a pivotal role in ensuring the subsequent trustworthiness and relevance of the data in use.
Engaging Users for Data Verification
To bridge the trust gap for unverified data, an interactive computer data object is generated, populated with query statements and approval options aligned to each unverified data file. Users, via their external computing devices, receive this data object, alongside an integrated view of their generated electronic data. Based on user inputs, the unverified data is updated and stored as newly verified files.
Rule-Driven Authenticity Checks
To ensure consistent and reliable data verification, a meticulous rules engine is utilized. This technology navigates a comprehensive set of rules, referencing dictionaries, and user verification protocols and plays a crucial role in confirming the authenticity of data by applying distinct rules tailored to various data categories.
Identity Verification
The importance of confirming a user’s identity is important because before any user data verification occurs, the technology ensures stringent identity verification, tapping into modalities like audio and image recognition, as well as location-based verification.
Streamlined Data Communication and Social Connectivity
After authenticating user data, it is integrated into an advanced transactional framework which not only preserves the data but also facilitates its communication across diverse computing points, reaching other users, service providers, and different entities. In addition, it adapts to dynamic social networking applications, which modify connections based on user interactions and authenticated data.
The technology ensures precise communication by dispatching electronic data messages to predetermined computing points, strictly following user permissions.
Elevating Data Integration and Trustworthiness
Beyond mere data processing, the technology amplifies the inherent value of user data. The user data, rich with embedded digital text, is displayed with clarity and uniformity. Each piece of verified data is further endowed with a trust score, indicative of its reliability and authenticity.
Machine Learning for Smart Data Categorization
Showcasing its progressive approach, the technology leverages machine learning. It identifies verification trends and autonomously sorts data into verified and unverified categories.
Facing the diverse challenges presented by user-generated electronic data, this technology’s functionalities deliver a holistic and dependable solution. It combines data acquisition, cloud integration, insightful data analyses, stringent identity checks, and machine learning insights to chart a course towards a more dependable and robust electronic data ecosystem.
