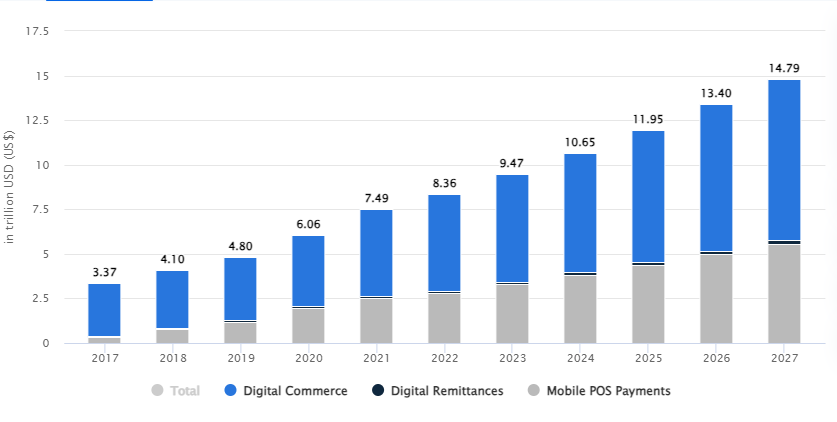
The Digital Payments market is set to witness significant growth in the coming years according to reports by Statista,. In 2023, the total transaction value in this sector is anticipated to reach US$9.46 trillion. This robust growth trend is expected to continue, with an estimated annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.80% from 2023 to 2027, bringing the projected total transaction value to a staggering US$14.78 trillion by 2027. A closer examination reveals that Digital Commerce dominates this market, with a forecasted total transaction value of US$6.03 trillion in 2023. On a global scale, China stands out as a frontrunner in the digital payments landscape, expected to amass a total transaction value of US$3,639.00 billion in 2023.
Top Innovations and Emerging Trends in Payment Systems Technology
Enhancing Payment Security
Companies in this space are investing significantly in authorization technologies to safeguard customer identities and verify payment details. With a staggering 1,115+ patent records in 2022, it’s clear that the industry is doubling down on efforts to enhance the trust and safety of digital transactions.
Going Wireless for Convenience
The rise of wireless technology has revolutionized the way we make payments. In 2022, companies recorded 919+ instances of innovations related to using wireless devices for payments as documented in patent assets. This shift towards wireless solutions has made payments more convenient and accessible for people on the go, reflecting the industry’s commitment to improving user experiences.
Crafting Seamless Payment Protocols
Behind the scenes, the intricate details of payment protocols matter greatly. With 800+ patent records dedicated to perfecting payment protocols, companies are streamlining and optimizing the way digital transactions are conducted. These innovations promise smoother and more reliable payment experiences for users.
Tailoring Marketing and Pricing
In the dynamic digital payment landscape, companies are placing an emphasis on marketing and price determination. With 567 patents in this category in 2022, businesses are constantly seeking more effective ways to estimate prices and raise funds. This trend indicates a keen interest in aligning payment solutions with the needs and preferences of customers.
Adapting for Electronic Funds Transfer
The year 2022 witnessed a surge in innovations tailored for electronic funds transfer (EFT) and home banking systems. With about 400 and 300+ records in these categories, respectively, companies are adapting their offerings to meet the changing needs of consumers. These advancements promise greater accessibility and efficiency in managing finances.
Exploring Private Payment Circuits
In the digital payment ecosystem, private payment circuits have gained prominence. These circuits, involving electronic currency used among participants of a common payment scheme, are seeing increased attention with 300+ patent records published only in 2022. Companies are looking to create closed-loop systems that enhance control and security in financial transactions.
Identifying the Gaps: Unexplored Opportunities in Digital Payments Industry
The digital payment landscape has witnessed significant transformation over recent years, as evidenced by the growth in patent filings. While patents serve as a clear indication of innovation and the direction in which companies are investing, they also reveal potential untapped opportunities or “whitespaces” that may reshape the future of this sector.
A close examination of the technology innovation timeline reveals that a predominant focus is on authorisation, particularly concerning the identification of payer or payee and verification processes. Wireless device authorizations indicates a clear whitespace in enhancing security measures for mobile-based payment systems. As mobile transactions surge in volume, fortifying these channels becomes crucial, thus presenting an ample space for innovation.
There is a considerable innovation in “Payment protocols,” further delineation might reveal opportunities for improved transactional efficiency or introducing novel protocols tailored for specific industries or transaction types. There seems to be room for growth and differentiation, especially when considering diverse global markets and their unique payment behaviors.
Furthermore, while there’s evident interest in electronic funds transfer and home banking systems, one can speculate that there’s potential for integrating more advanced and alternative payment technologies. The inclusion of AI-driven insights, blockchain-backed transparency, or even leveraging IoT for real-time banking might offer the next frontier in this technology cluster.
Top Challenges and Overcoming Them in Today’s Digital Payment Technologies
Traditional payment systems, despite their adoption and familiarity, come with a range of challenges:
1. High Transactional Costs: Traditional payment systems often involve multiple intermediaries, each levying their own processing fees. These fees can significantly increase the cost of transactions, especially for small-scale transactions or for businesses operating on thin margins. Alternative payment technologies can focus on eliminating the need for multiple intermediaries as a medium of exchange. This can effectively reduce, or in some scenarios, completely removes transaction fees. The cost-saving potential for both consumers and businesses is substantial.
2. Delayed Processing Times: In many conventional payment mechanisms, especially those involving cross-border transactions, processing can take several days due to multiple verification processes and the involvement of various intermediaries. Innovative methods may allow for instantaneous or near-instantaneous processing. New models of payments can simplify the transaction chain, expediting the overall transaction time.
3. Security and Fraud Concerns: Traditional payment systems are frequently targeted by cybercriminals, leading to data breaches, unauthorized transactions, and other security concerns. Such breaches can result in financial losses and diminish consumer trust. New technologies must emphasize on advanced encryption techniques and stringent privacy controls. By transitioning to a model where personal financial information is not exchanged, the system inherently reduces the potential attack vectors for traditional financial fraud.
4. Accessibility and Inclusion:
A substantial fraction of the population remains disconnected from conventional financial systems. These unbanked or underbanked individuals often reside in regions with limited banking infrastructure or belong to demographics that are underserved by traditional financial institutions. As a result, they face barriers in accessing many modern goods and services that require formal financial channels, effectively excluding them from the broader digital economy. The ubiquity of digital technology, even in regions with limited banking infrastructure, has led to a scenario where nearly every individual, regardless of their banking status, generates some form of data. This could be derived from mobile interactions, online searches, application usage, and other digital footprints. A “pay through data” model can harness this universally generated data as a valuable asset.
Under this system, the data an individual creates, rather than money in a conventional sense, becomes a currency. It’s a currency that doesn’t discriminate based on one’s location, economic status, or access to banking facilities. By offering their data in exchange for goods and services, these previously excluded individuals now have a gateway to participate in the digital economy. This not only democratizes access to services but also promotes a more inclusive digital ecosystem, where one’s value is recognized not just by monetary wealth, but by their digital interactions and contributions.
5. Currency Conversion Complications: For international transactions, currency conversion introduces additional challenges, from unfavorable exchange rates to added fees, making such transactions expensive and complex. The universal nature of data eliminates the need for currency conversion. Whether a user is in Asia, Europe, or the Americas, their data holds value. By using this data as a medium of exchange, businesses can offer services without grappling with the complexities of currency conversion.
In conclusion, the patented “pay through data” technology as discussed below not only presents an innovative solution to the challenges plaguing traditional payment systems but also provides a new era in digital transactions. The potential to redefine transactional dynamics, while addressing inherent issues of the conventional systems, underscores the transformative potential of this approach.
Exploring Beyond Crypto and Payment Cards: The Need for Breakthrough Payment Systems
To better appreciate the need for revolutionary payment systems, one must consider the statistical landscape of the current payment paradigms. According to a 2021 World Bank report, around 1.7 billion adults remain unbanked, not having an account at a financial institution or through a mobile money provider. Meanwhile, the International Telecommunication Union in 2020 highlighted that 53% of the global population has internet access, emphasizing the large number of individuals generating data daily. Much of this innovation, as chronicled in patents and industry practices, has centered around two paradigms: cryptocurrency and card-based systems.
Cryptocurrencies, with their decentralized nature and cryptographic security, promised a transformative shift from traditional banking. They’ve allowed peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries, presenting a decentralized future for financial exchanges. On the other hand, card-based payment systems, both physical and virtual, have undergone a series of advancements to optimize transaction speeds, enhance security measures, and integrate with various service platforms.
While these innovations have unquestionably reshaped facets of the payment landscape, they haven’t fully addressed all the gaps and challenges inherent to the current systems. Despite the strides made, significant portions of the global population remain alienated from these advanced payment mechanisms due to various socio-economic and infrastructural constraints.
There exists a need to explore beyond the familiar terrains of crypto and cards. The current landscape beckons for groundbreaking systems that don’t merely iterate on existing models but radically reimagine the very essence of transactions. Our patent portfolio underscores this sentiment by advocating for a paradigm where user-generated data, a ubiquitous and untapped asset, is positioned at the epicenter of transactions, effectively serving as a novel medium of exchange.
This breakthrough approach not only broadens the horizons of payment methodologies but also paves the way for previously inconceivable opportunities. By leveraging the intrinsic value of user data, this new system can create a more inclusive, efficient, and equitable digital economy, catering to demographics that current models might inadvertently overlook. The vast potential of this patent emphasizes the untapped avenues in the payment sector and underscores the urgency and significance of diversifying innovation in this space.
Evolving importance of data
The importance of data in the contemporary world is escalating, cementing its position not only as a driver of business decisions but also as a crucial asset in almost every sector. Here’s a dive into the evolving significance of data, supplemented by recent insights and statistics:
Evolution of data: By 2025, the global datasphere is expected to grow to 175 zettabytes (1 zettabyte = 1 billion terabytes), reflecting the explosive growth in data generation.
Economic Value: Data has rapidly become a cornerstone of the global economy, with its economic valuation skyrocketing into the trillions, reshaping industries and businesses.
AI and Machine Learning: The vast majority of the world’s data has been generated recently, fueling the growth of AI and Machine Learning as key tools to extract actionable insights.
Healthcare Revolution: The COVID-19 pandemic accentuated the critical role of data in healthcare. Real-time data analytics helped manage and understand the spread, establishing data as an essential tool in health crises.
Personalization in Marketing: Modern consumers expect and respond positively to personalized experiences, indicating a shift in marketing strategies towards data-driven personalization.
Data Privacy and Regulations: The increasing significance of data has led to the formulation of stringent data protection regulations worldwide, underscoring the need for responsible data management.
Decision Making: Organizations across the globe are investing heavily in data-driven strategies, signifying a recognition of data as a foundational asset for informed decision-making.
Environmental Monitoring: Data plays an instrumental role in monitoring environmental variables and phenomena, providing insights into climate patterns, deforestation, and more.
Smart Cities: Urban centers are leveraging data to transition into ‘smart cities’, aiming for optimized operations and enhanced quality of life for residents. Predictions indicate that the smart city market will see substantial growth in the coming years due to data-driven innovations.
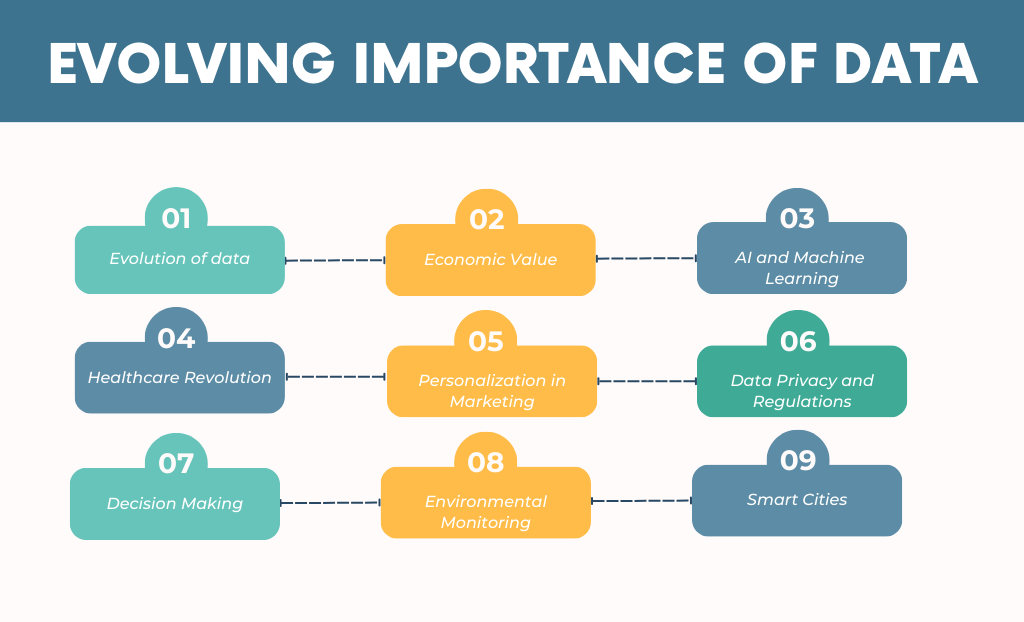
The pervasiveness of data and its growing importance cannot be understated. As industries, governments, and individuals continue to generate and harness data, it is clear that this trend will only ascend, underpinning a myriad of applications and innovations in the years to come.
Leveraging User Data as Currency in Digital Payment Transactions
Each digital interaction, search query, transaction, or behavior logged by a user represents a potential source of information that, when aggregated and analyzed, yields insights that are of substantial value to various industries. Recognizing this inherent value, our patented technology presents a pioneering framework for understanding and leveraging this data as an alternative to traditional monetary systems.
-
Quantification of Data Value: The patent introduces methodologies to evaluate the intrinsic worth of user data. Just as monetary units (e.g., dollars, euros) have a determinable value in the market, the patent’s mechanisms provide algorithms to determine the comparative worth of specific datasets. This quantification allows for data to be viewed and exchanged as one would with traditional currency.
-
Data as a Transactional Medium: With its value established, user data can serve as a medium of exchange. Instead of relying solely on traditional currencies, users could potentially offer their data in exchange for goods, services, or access. The patent elucidates the structures and protocols required to facilitate such exchanges securely and transparently.
-
Security and Authenticity: A major concern with introducing a new transactional system is ensuring the security and authenticity of exchanges. The patent incorporates advanced encryption and verification techniques to ensure that data exchanges remain confidential and tamper-proof, akin to secure monetary transactions.
-
Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Considerations: The patent also considers the ethical implications and regulatory requirements associated with data transactions. By establishing clear protocols for user consent and data usage, the system ensures that data exchanges are conducted in an ethically sound and legally compliant manner.
-
Interoperability with Traditional Systems: Recognizing that a transition to a data-centric transaction system would be incremental, the patent outlines mechanisms by which user data exchanges can coexist and integrate with traditional monetary transaction systems.
-
Market Dynamics and Data Liquidity: Just as financial markets determine the value of currencies based on demand, supply, and other economic indicators, the patent envisions a dynamic ecosystem wherein the value of data can fluctuate based on its relevance, rarity, and demand. This introduces the concept of ‘data liquidity,’ indicating how readily a particular dataset can be exchanged in the market.
This innovative patented system holds a transformative approach to digital transactions, recognizing user data not merely as passive information but as a potent asset with quantifiable value. By providing the tools, mechanisms, and frameworks necessary, the patent paves the way for a future where data could seamlessly serve as an alternative or complement to traditional currencies in the digital marketplace.
Leveraging Diverse Data for Enhanced Payment Solutions
Within the intricate web of digital interactions, each user generates a diverse array of data, both overtly and implicitly. This multifaceted data mosaic is not merely a passive digital footprint but holds valuable insights that can be beneficial for various stakeholders. In the context of our patented system, which focuses on the exchange of user data for processing of payment, it’s pivotal to understand the types and potential applications of this data.
-
Behavioral Data: This captures a user’s interactions, preferences, and patterns within digital ecosystems. For instance, the sequence and duration of actions on an application or website can offer insights into user behavior, which can be invaluable for interface optimization or marketing strategies.
-
Transactional Data: Each purchase, click, or interaction within a digital commerce space creates data points. This data can help in understanding purchasing behavior, preferences, and loyalty, which is central to our patented approach where such data can potentially be utilized as a form of payment.
-
Demographic Data: Details such as age, gender, location, and occupation offer a macro view of a user’s profile. When intertwined with our patented system, businesses can tailor their offerings or services based on these demographic insights, further incentivizing users to share their data.
-
Feedback and Reviews: Direct user feedback, reviews, or ratings are pure gold for businesses. They provide candid insights into product or service quality, user satisfaction, and areas of improvement. In our system, such data can be a component of the transaction, giving businesses valuable feedback in exchange for services or goods.
-
Sensor-generated Data: With the proliferation of wearable devices and smartphones, users generate data related to health metrics, location, movement patterns, and more. This data, when integrated into our patent’s framework, can offer businesses insights into user lifestyles, allowing for more tailored services.
-
Communication Data: Metadata from user communications, like frequency, timing, or mode of communication, can be utilized to understand user habits. While always prioritizing privacy, our patented system can leverage such data for transactions, offering value both to users and service providers.
Incorporating the above data types into our patented exchange system, we’re not just facilitating a transaction; we’re fostering a symbiotic relationship. Users get the services or goods they seek, while businesses gain invaluable insights that can drive optimization, innovation, and growth. This paradigm shift, from a mere transactional approach to a holistic data exchange model, underscores the latent potential of user data and its diverse applications when harnessed judiciously and ethically.
Data-Driven Transactions: Charting the Future of Digital Commerce
Rather than relying solely on traditional financial transactions, we envision a system where users exchange their valuable data for services and goods.
Opportunity Outline: Data as Currency
Every click, purchase, social media interaction, and online search generates data. With the right infrastructure and ethical considerations, this data has potential value, akin to monetary currency. Here’s a glimpse into the scale and potential of this emerging opportunity:
-
Potential Market Size: According to the International Data Corporation (IDC), the collective sum of the world’s data, termed the “Global Datasphere”, was poised to grow from 33 zettabytes (ZB) in 2018 to a projected 175 ZB by 2025. With such exponential growth, even if a fraction of this data is utilized in the proposed exchange model, it represents a multi-billion dollar opportunity.
-
Emerging Consumer Preferences: A survey conducted by the Pew Research Center indicated that 72% of people felt that almost all of what they did online was being tracked by advertisers, technology firms, or other companies. However, if users could tangibly benefit from this tracking in the form of direct exchanges for goods or services, perceptions might shift more favorably.
-
Pioneering Sectors: Industries like healthcare, where users generate heaps of data through wearables and health apps, are ripe for such an exchange model. The global digital health market value was estimated at around $96.5 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow further. If even a fraction of this industry adopted a data-for-service model, it could pioneer a substantial economic shift.
-
Operational Efficiency for Businesses: Traditional payment gateways often involve transaction fees and delays. A data-exchange system could streamline this, making operations more efficient and cost-effective for businesses.
-
Inclusive Economics: Nearly 1.7 billion adults remain unbanked globally, according to the World Bank. However, many of them have access to mobile phones and thus generate data. This model could pave the way for including this significant population segment in the global digital economy.
-
Customization and Personalization: With direct access to user data, businesses can offer highly personalized experiences, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
While the notion of exchanging data for services and goods is still in its nascent stages, the potential it holds is enormous. If navigated ethically, transparently, and innovatively, this model could redefine transactional relationships, creating a new frontier in the digital economy. It would not only monetize the vast reservoirs of user-generated data but also provide tangible value back to the users, thereby creating a more symbiotic digital ecosystem.
Leap in Digital Transactions: Our Patented Innovation
The untapped opportunity of leveraging user data as a form of payment holds immense potential. In response to this observed trend, our patented system introduces an innovative computational mechanism. Operating in a digital environment, where data attributes and electronic transactions constitute foundational elements, this algorithmic payment system quantitatively integrates data valuation with transactional parameters. The core mechanism hinges on an advanced computational engine, adept at calculating transactional outcomes based on a stratified digital transactional model. This encompasses service charges, predefined co-pays, and the fundamental data worth. Enhanced by components like the service interaction element and a remotely located pre-consenting system, our platform promises secure, efficient, and revolutionary transactions, charting an uncharted trajectory in the digital payment domain.
The patent portfolio details a digital payment system controlled by a computer. It facilitates smooth transactions between a user and a buyer, with the assistance of an intermediary, in a particular setting, like a service venue or platform.
A digital service provider, much like an online platform, equipped with the necessary technology, including cloud computing capabilities, can deliver a service to its users. This provider can send signals to a user’s device, allowing them to communicate and interact. Through this interaction, the provider collects basic information about the user and their device, as well as what specific service they are seeking.
An essential feature of this system is its ‘payment engine’. This isn’t just about processing traditional payments. It can determine how much a user owes based on several factors. First, there’s the basic charge for the digital service. Then, there might be an additional shared cost or co-pay. Interestingly, the third factor is the value of the user’s data that they are willing to share. This data’s worth is defined based on criteria set by the buyer, considering various types of data and attributes.
The system also has a separate component, known as the ‘pre-consenting system’. Its primary role is to get permission from users in advance before their data is used in a transaction. Once this permission is given, the system recognizes it, creates a unique code for that user, and then safely handles, processes, and shares the user’s authorized data.
This patented system doesn’t just allow for straightforward digital payments but also factors in the value of user data, ensuring that any data use or sharing is done with prior consent, enhancing both flexibility and trust in digital transactions.
An excerpt from patent claim.
“A computer-controlled payment system for facilitating seamless transactions from a user system to a buyer system via an intermediary system, the system comprising:
an electronic service provider system associated with a service provider and located physically in a service setting that includes one or more central servers, data stores, and cloud-based computing components for managing and processing delivery of a service in the service setting by the service provider to the user associated with the user system, wherein the service provider system comprising:
a service interaction component to generate an electronic signal transmitted to the user system using a transmission circuit, and wherein the electronic signal allows communication between the user system and the service provider system, the service interaction component further configured to collect predefined information about the user system and the associated user, the predefined information comprising at least a first computer-executable input indicative of an identifier of the user system and the associated user and a second computer-executable input indicative of a service sought for delivery in the service setting by the service provider; and
a payment engine for processing payments digitally based on data worth associated with the data owned by the user and authorized for sharing by the service provider to the buyer system, wherein the payment engine calculates a payable amount payable digitally by the user to the service provider based on:
a first digital transactional value indicative of a service charge for the service delivered digitally by the service provider;
a second digital transactional value indicative of a predefined co-pay between the user and a co-pay entity; and
a third digital transactional value indicative of the data worth associated with the data owned by the user and authorized for sharing,
wherein the data worth is calculated based on a set of predefined criteria specified by the buyer entity for a set of data types, data entities and data attributes; and
a pre-consenting system located remotely from the user system and communicatively coupled to the service provider system in the service setting, wherein the pre-consenting system is configured to receive a digital signal containing a third computer-executable input for authorizing sharing of the data owned by the user at least in part toward a digital purchase and delivery of the service from the service provider by the user such that the data owned by the user serves as a transactional value for the digital purchase and delivery of the service as and when the data is made available,
wherein the pre-consenting system is further configured to generate a trigger that is initiated upon electronic receipt of the third computer-executable input by the pre-consenting system, the trigger containing a unique code referencing the user, the user system and authorized data of the user for storage, processing, and sharing of the authorized data.”
Read the original patent here.
Read layman patent summary here.
Advancing Digital Payments: Solving Transaction Challenges with Patented Technology
The patented technology addresses these pain points by offering a realistic and feasible solution that seamlessly integrates data worth into the digital transaction process, backed by robust consent management and communication systems, ensuring operational efficiency, security, and optimized value extraction.
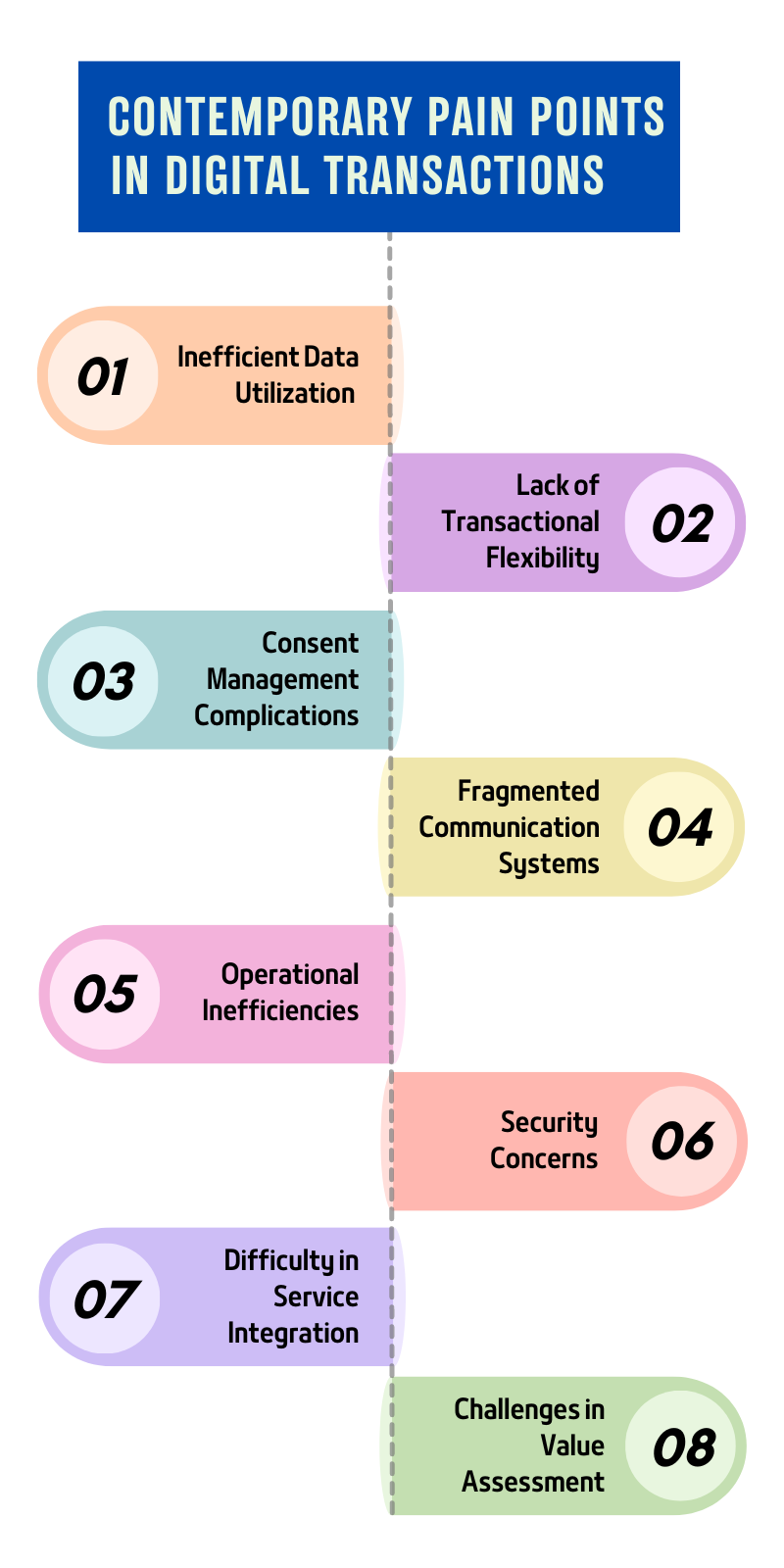
-
Inefficient Data Utilization: In sectors where data holds significant value — both intrinsic and monetary — traditional systems often fail to adequately leverage this asset. Industries lose out on potential revenue streams and optimization opportunities by not quantifying and utilizing the worth of user data during transactions.
-
Lack of Transactional Flexibility: Traditional payment methods may not accommodate the dynamic nature of digital service charges, co-pays, and data-related transaction values. As a result, providers face challenges in offering flexible pricing structures or customizing service offerings based on data-driven insights.
-
Consent Management Complications: Industries that heavily rely on user data often grapple with obtaining explicit, informed consent for its use, especially in real-time transactional scenarios. Without a streamlined pre-consenting mechanism, providers face potential regulatory pitfalls and trust issues with users.
-
Fragmented Communication Systems: A consistent pain point across sectors is the inability of older systems to effectively communicate with modern digital infrastructures, leading to incomplete data exchanges, potential misunderstandings, and transactional errors.
-
Operational Inefficiencies: Slow and cumbersome transaction processes can bottleneck operations. In scenarios where immediate data validation and payment processing are crucial — such as in healthcare or on-demand services — delays can severely impact service delivery and customer satisfaction.
-
Security Concerns: As transactions become more intertwined with data exchanges, the risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized access, or misuse magnify. Traditional systems might not be equipped with the requisite security protocols to handle these intricate transactions.
-
Difficulty in Service Integration: Providers often struggle to integrate various services into a singular transactional process. For example, in sectors like healthcare, where a single user interaction might involve consultations, diagnostics, and medication purchases, managing these as separate transactional entities can be cumbersome and inefficient.
-
Challenges in Value Assessment: Determining the ‘worth’ of data in transactional terms is a nuanced process, requiring sophisticated algorithms and valuation metrics. Many industries lack the tools or methodologies to accurately assess this, leading to potential undervaluation or missed revenue opportunities.
The Strategic Role of Intellectual Property Assets in Payment System Technologies
The development and acquisition of intellectual property (IP) assets plays an important role in the competitive landscape of payment systems, particularly in the space of alternative payment methods. As technological advancements continue to drive the evolution of payment platforms, holding strategic IP assets becomes instrumental in safeguarding innovations, fortifying market presence, and providing a distinct competitive advantage. The fact that as many as 4,144 patents were published in the year 2022 alone in payment technologies underscores the heightened emphasis on innovation and the race among enterprises to secure their advancements in this dynamic sector.
For companies operating in the sphere of alternative payment systems, these IP assets not only signify a robust commitment to innovation but also offer a strategic vantage point in negotiations, partnerships, and potential market expansions. They serve as tangible markers of a company’s foresight, readiness, and adaptability in an industry marked by rapid technological shifts. Moreover, in a domain where trust and security are paramount, a solid IP portfolio can enhance stakeholder confidence, affirming a company’s dedication to pioneering safe and efficient payment solutions for the future.
Leading Innovators in Digital Payment Systems: Key IP Developers of 2022 and Their Target Market and Synergy with Our Patented Portfolio
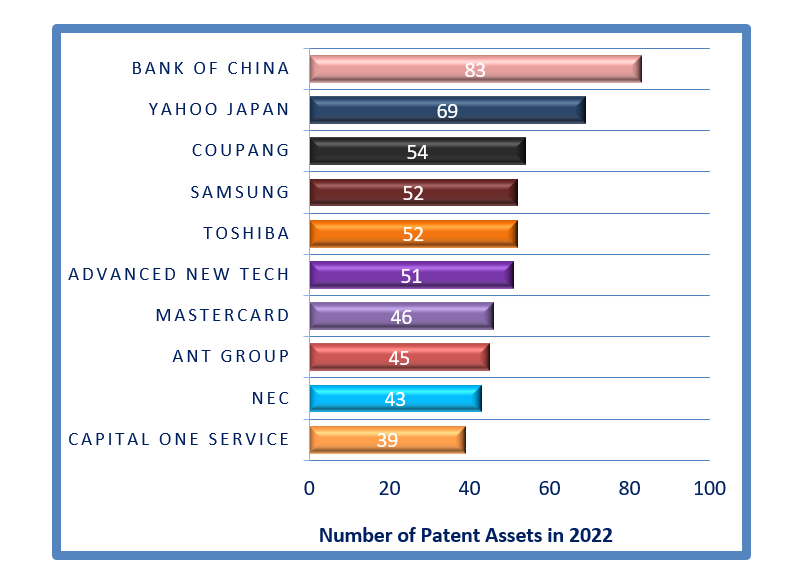
[Source: Intellectual Frontiers Innovation Report]
Filling the IP Whitespaces - The Impact of Our Patent Portfolio on Enhancing the Current Payment Systems Landscape
Recognizing this potential, our patented ‘Pay through data’ approach offers a groundbreaking shift from traditional transaction paradigms. The patented technology enables companies to derive dual benefits from a single transaction: direct monetary compensation and invaluable user data. By monetizing the intrinsic worth of data and intertwining it with the conventional payment structure, businesses can gain a multi-dimensional understanding of their consumers, opening doors to targeted service offerings, and personalized user experiences.
Furthermore, by adopting the ‘Pay through data’ system, companies can position themselves ahead of the curve, tapping into the evident whitespaces in the current market landscape. While many businesses are still grappling with the challenge of effective data utilization, this technology provides a ready-to-implement solution, ensuring that companies not just remain relevant but lead in their respective domains. In essence, it offers businesses a dual advantage - a tangible competitive edge and a blueprint to harness untapped market opportunities, setting the stage for sustained growth and innovation.
The publication of an astounding 20,951 patent records during this period serves as a testament to the fervor with which businesses have pursued technological advancements and novel strategies in payment solutions. This uptick in patent filings underscores the industry’s commitment to enhancing transactional efficiency, security, and user experience, responding dynamically to the ever-evolving consumer needs and market trends. With each patent symbolizing a unique stride forward, the cumulative intellectual contributions offer a comprehensive overview of a sector that is unceasingly pushing the boundaries, setting new benchmarks, and pioneering the future of financial transactions.
Our patented technology certainly adds to the strength of the current patent landscape in digital payments industry.
Opportunities for the Patented Automated Payment System across Multiple Industries
This system is an innovative payment engine that calculates transactional values based on a combination of service charges, co-pays, and the intrinsic worth of the user’s data. By quantifying the value of data and incorporating it into the payment equation, the system brings forth an unprecedented level of flexibility and adaptability to the transaction process. This is further enhanced by a robust pre-consenting system, ensuring that user data is not just utilized but is done so with explicit permission, enhancing trust and ensuring compliance.
Healthcare: In an industry like healthcare, where every patient interaction generates a range of valuable data, our system promises change from consultations and diagnostics to medication purchases, the system ensures seamless transactions by integrating various services into a singular process. The dynamic nature of the payment engine allows for customized service offerings, optimizing both revenue streams for providers and the value derived by patients.
E-Commerce: The e-commerce industry, which thrives on user data for personalized marketing and product recommendations, stands to benefit immensely. With our patented, online platforms can offer dynamic pricing structures based on user data worth, transforming the very nature of online shopping experiences.
Banking and Finance: In an age where financial institutions are investing heavily in data analytics and personalized banking experiences, our system can introduce novel transactional models, where data insights and user profiles determine transactional values, offering tailored financial solutions to users.
Telecommunications: As telecom operators grapple with dwindling traditional revenue streams, our system offers a unique opportunity. By quantifying the worth of user data related to usage patterns, preferences, and behaviors, telecom operators can introduce dynamic pricing models, enhancing customer retention and driving profitability.
Travel and Hospitality: For industries relying on personalization, such as travel and hospitality, our payment system can redefine loyalty programs and booking experiences. By integrating user preferences, past travels, and feedback into the transactional value, businesses can offer bespoke packages and deals, enhancing user satisfaction and loyalty.
In conclusion, our automated digital payment system isn’t just a solution; it’s a paradigm shift. It bridges the gap between the tangible world of transactions and the intangible world of data, promising a future where every byte of data holds quantifiable value, ready to be seamlessly integrated into our daily transactions across various industries.
Our patented system stands as a epitome of innovation in harnessing user-generated data. Through algorithmic processes and a robust computational framework, the system facilitates the assimilation of diverse data modalities into a cohesive transactional mechanism. By converging behavioral, transactional, demographic, feedback, sensor-generated, and communication data, it offers an unparalleled granularity in understanding user dynamics. Furthermore, the emphasis on ethical data handling, coupled with advanced encryption methodologies, ensures the integrity and confidentiality of user data. This multifaceted approach not only circumvents the limitations of traditional payment systems but also positions our patented system at the forefront of the impending data-driven transactional revolution. In essence, this pioneering initiative epitomizes the synthesis of data science and digital commerce, marking a transformative phase in the realm of electronic transactions.
Read the original patent here.
Read layman patent summary here.
Should you be interested in licensing or purchasing this patent portfolio to strengthen your position in this evolving technological landscape, or if you have any inquiries or require additional material, please contact us at hello@intellectualfrontiers.com.
