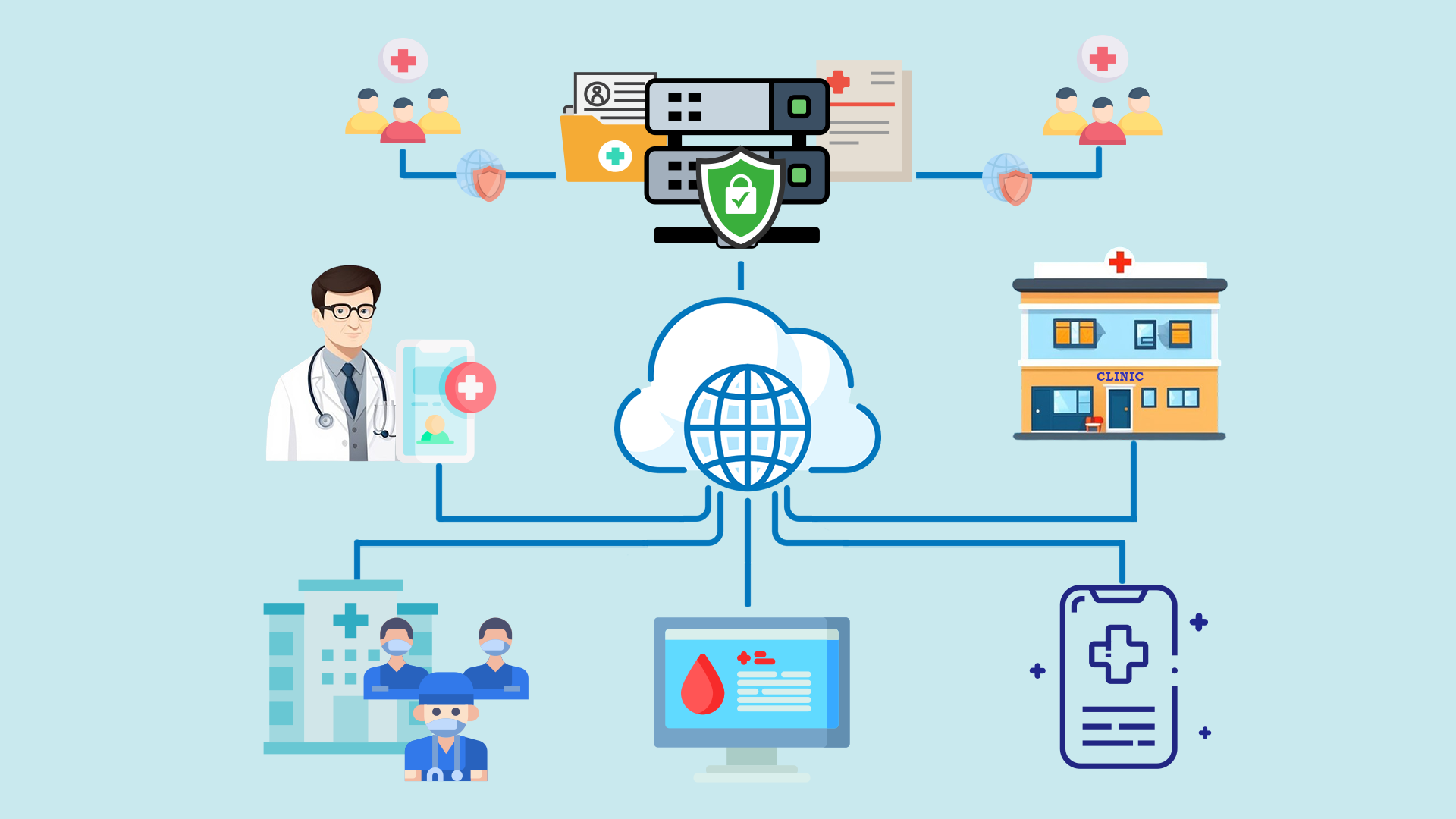
The Evolution of Electronic Records
Electronic records signify digitally documented information specific to individual users or owners. Such records, ranging from financial and healthcare data to information services, are curated by professionals, including physicians, analysts, and specialists. The information holders, like patients, document and safeguard their data. Modern technology has facilitated the storage of this confidential data in centralized databases, making it easily accessible over internet-based platforms. This ease of access carries inherent risks, when external devices or third-party entities express interest in accessing these records.
The Need for Advanced Self-Authorization Mechanisms
The rapid expansion of electronic records in recent years has brought with it a host of challenges, not least of which is the issue of authorization. As more information becomes digitized and stored online, the task of controlling who can access it becomes more intricate. One cannot overlook the presence of regulatory frameworks like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPPA). This act, specifically, underscores the significance of safeguarding health-related information, highlighting the critical nature of controlled access to such sensitive data.
Smaller datasets have traditionally been less concerning. Typically, the direct permission of the data owner or a simple access code might be enough to grant entry. This streamlined approach works effectively when the scope of the data is limited and the number of potential access requests is manageable.
However, the landscape changes considerably as the volume of electronic records balloons. Suddenly, you’re not just dealing with a few records that can be easily monitored. The vast amount of data makes it difficult for companies to identify relevant information swiftly. This surge also magnifies the challenges of ensuring that only legitimate requests are granted access, especially when considering the multitude of potential security threats in the digital age.
To address these challenges, robust systems and protocols are necessary. It’s no longer just about storing data but about smart storage. The mechanisms for pinpointing specific data, authorizing access, and, most crucially, ensuring that these authorizations are both secure and compliant with legal requirements, are essential in today’s data-driven world.
Introducing the Self-Controlled Digital Authorization Technology
Data access and security are paramount today. A Self-Controlled Digital Authorization Technology offers a breakthrough. This cutting-edge solution prioritizes user-defined conditions and regulatory guidelines to grant or deny access to computerized records. By considering geographical constraints, validating entity credentials, and continually monitoring access patterns for anomalies, it ensures a balanced blend of accessibility and protection. As the digital world grows, harnessing such innovative self-authorization techniques is crucial to maintaining the integrity and safety of our electronic data landscape.
Advanced Functionalities of the Digital Authorization Technology
This technology offers a sophisticated solution to safeguard digital records by relying on several layers of authorization and evaluation.
Stores Digital Profiles : Every subject gets a unique digital identifier, streamlining data management and retrieval.
Applies Adaptive Rules : Beyond basic permissions, the system considers both static device information and dynamic contextual factors to dictate access.
Utilizes Location-Based Access : Devices are tracked via GPS, and access rights dynamically adapt based on the user’s location, ensuring both flexibility and security.
Employs Community Trust Metrics : By gathering feedback from a diverse set of users, the system establishes a trust score for each device, making collective wisdom a part of its decision-making.
Learns Behavior Over Time : Recognizing patterns in device behavior, it calculates a consistency metric, allowing or denying access based on how aligned a device’s actions are with its historical behavior.
Delivers Comprehensive Decision-Making : The system combines insights from location tracking, trust metrics, and behavior analysis to make holistic access decisions.
Optimizes for Seamless Integration : Once access is granted, digital records are optimized for immediate and effortless integration with associated devices.
By amalgamating multiple sophisticated functionalities, this Digital Authorization Technology ensures meticulous, context-sensitive, and secure access to digital records, providing user convenience with paramount security measures. The technology signifies a change in how we approach the digital authorization of computerized records and by weaving together geolocation-based rules, trust scores sourced from the wider community, and a behaviour-centric approach. It provides a nuanced and robust system that is adaptable to varying contexts. This technology acts as a testament to innovation that prioritizes both user accessibility and data protection.
